AP Literature vs. AP Language
Students have a choice when it comes time to pick their English class for their senior year at TJ. This table explains the difference between AP English Literature and Composition vs. AP English Language and Composition.
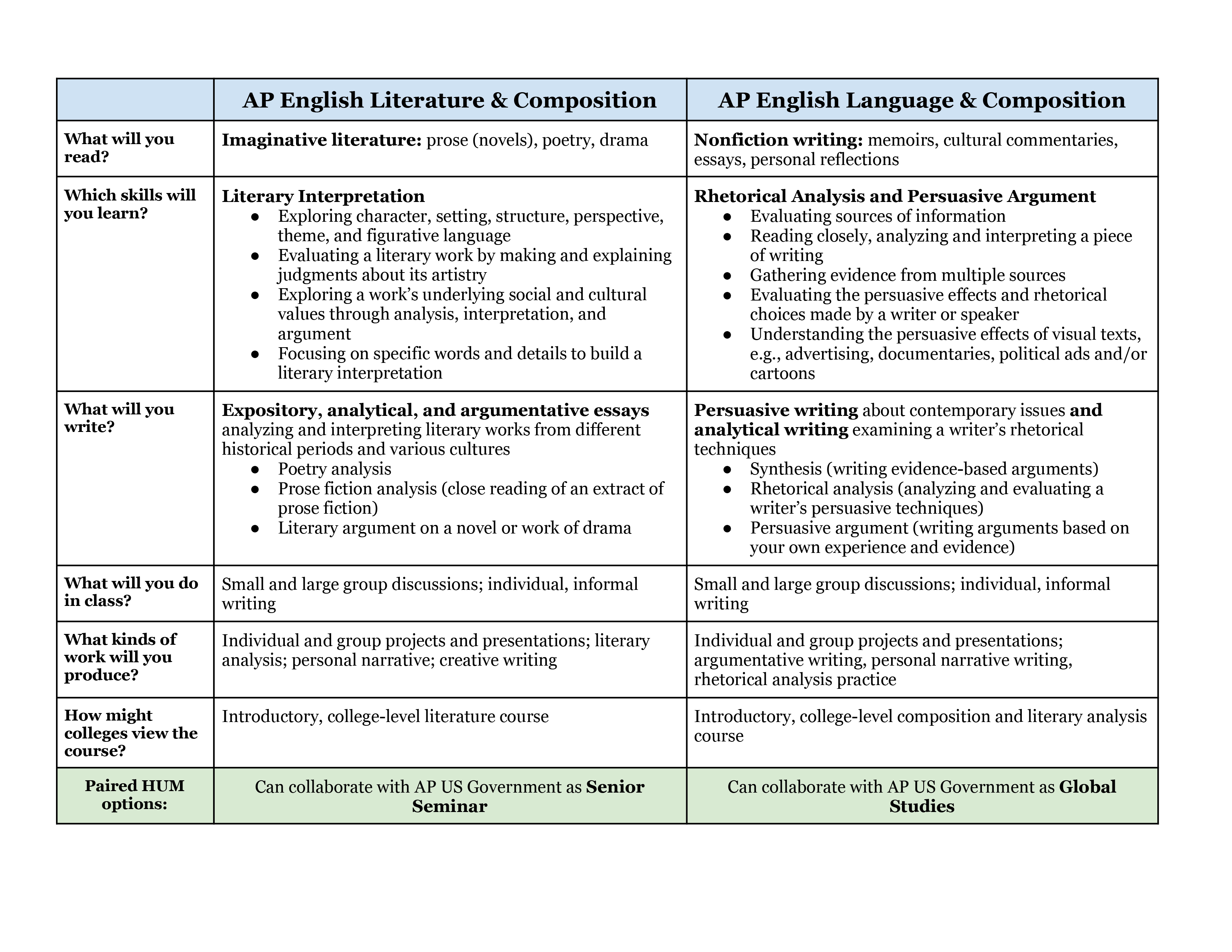
The information in the above picture is typed out below:
| AP English Literature & Composition | AP English Language & Composition | |
| What will you read? | Imaginative literature: prose (novels), poetry, drama | Nonfiction writing: memoirs, cultural commentaries, essays, personal reflections |
| Which skills will you learn? | Literary Interpretation
| Rhetorical Analysis and Persuasive Argument
|
| What will you write? | Expository, analytical, and argumentative essays
| Persuasive writing about contemporary issues and
|
| What will you do in class? | Small and large group discussions; individual, informal writing | Small and large group discussions; individual, informal writing |
| What kinds of work will you produce? | Individual and group projects and presentations; literary analysis; personal narrative; creative writing | Individual and group projects and presentations; argumentative writing, personal narrative writing, rhetorical analysis practice |
| How might colleges view the course? | Introductory, college-level literature course | Introductory, college-level composition and literary analysis course |
| Paired HUM options: | Can collaborate with AP US Government as Senior Seminar | Can collaborate with AP US Government as Global Studies |

